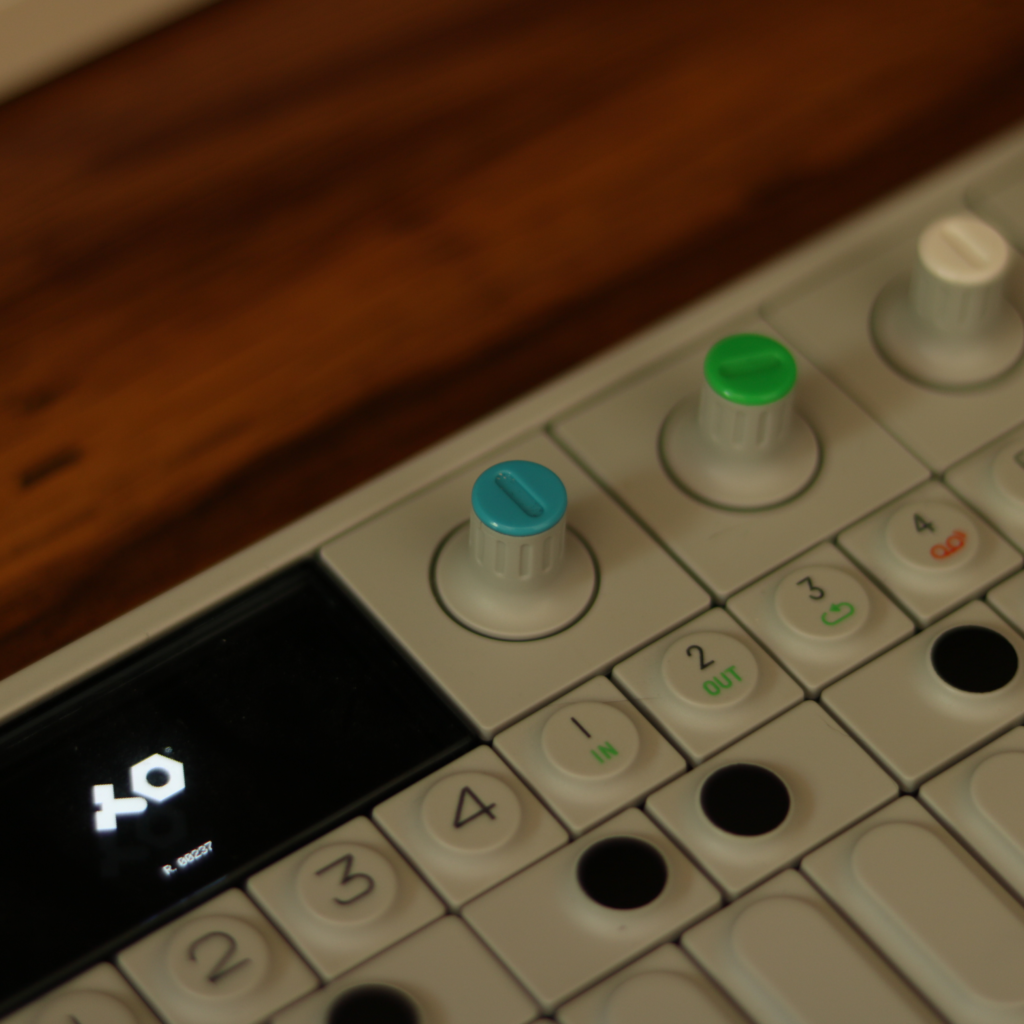
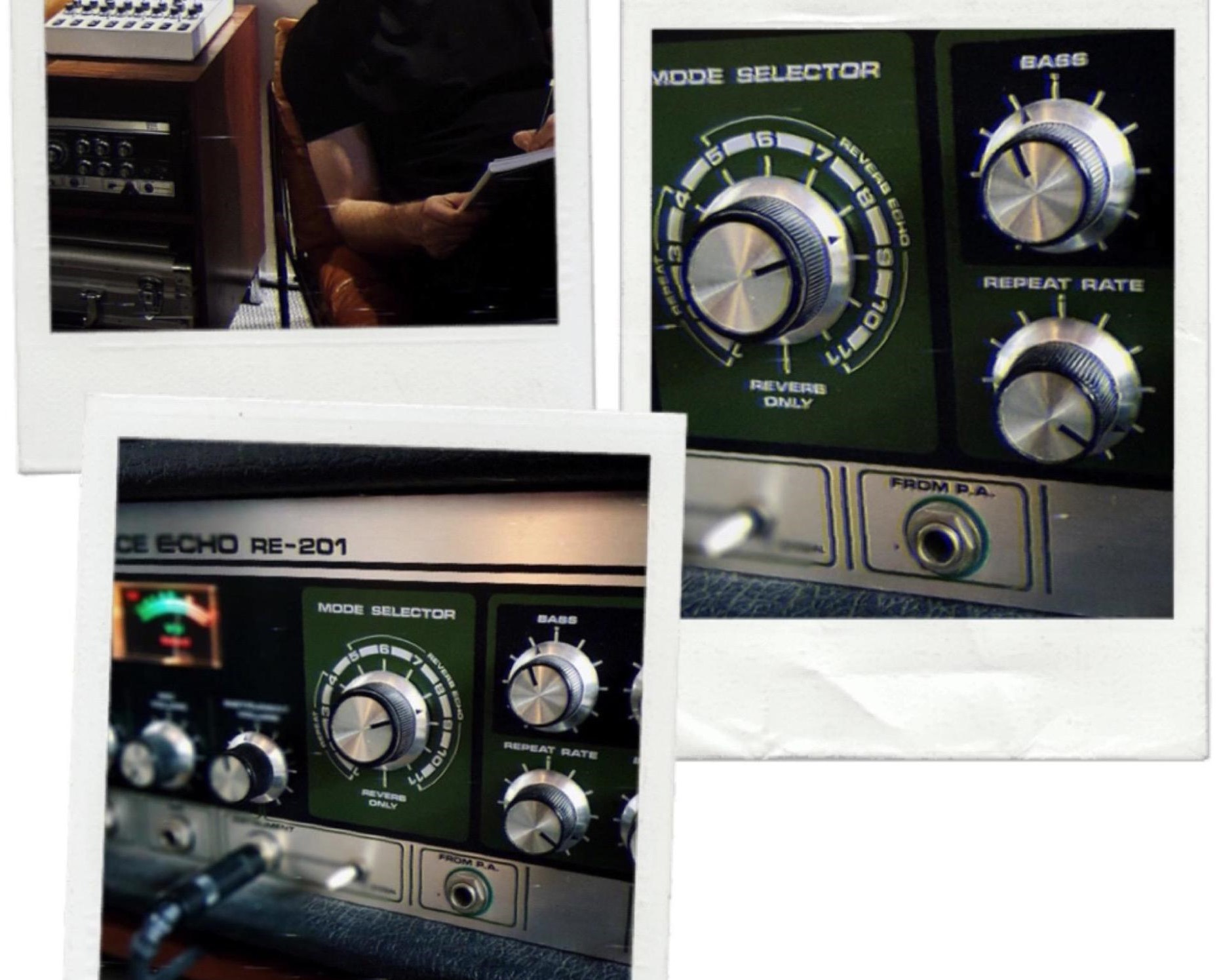
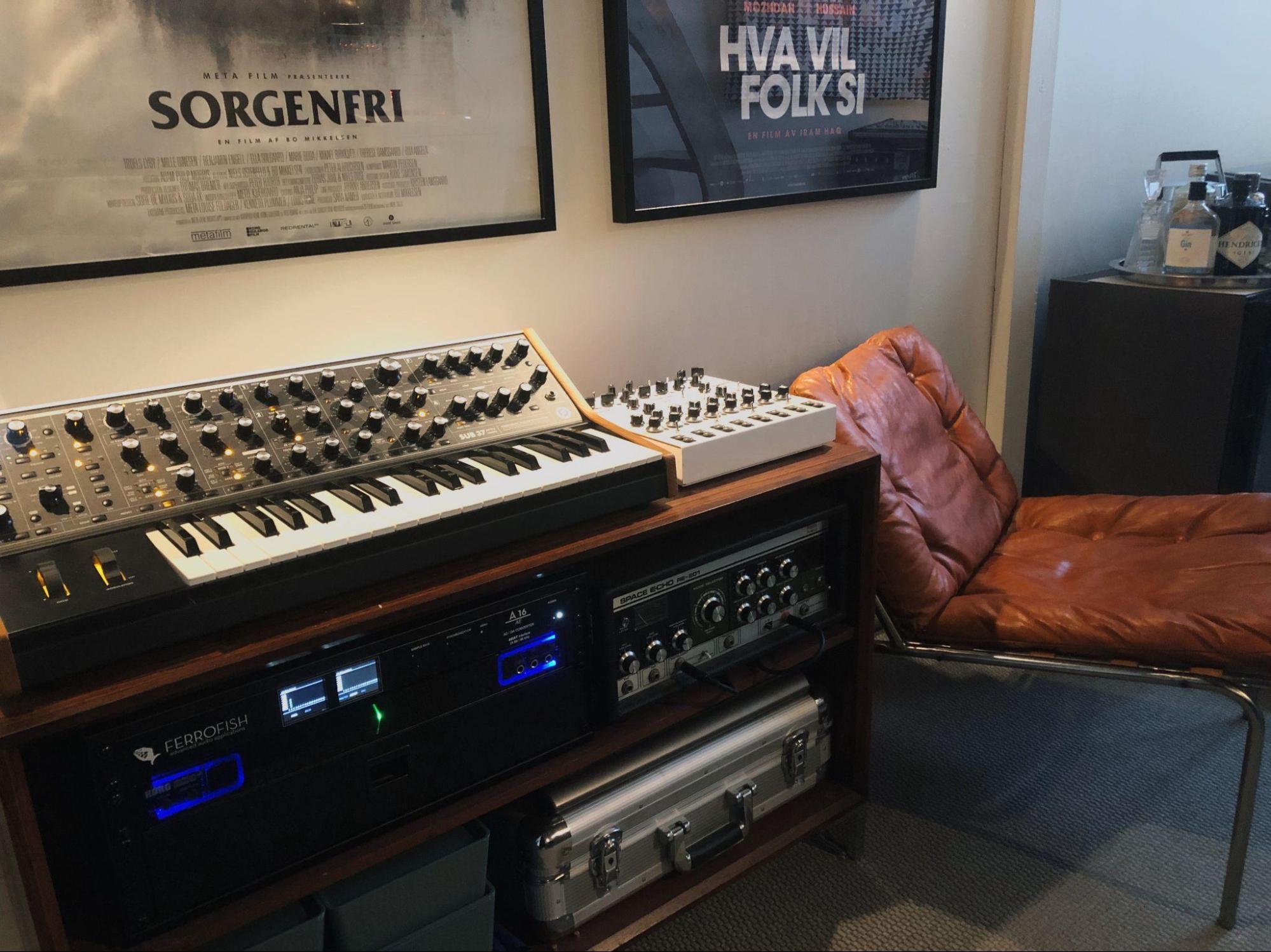
1. Favorite knob or fader or switch on a piece of gear and why?
Space Echo RE-201 Mode Selector knob. Do you really need an explanation… Just look at it:)

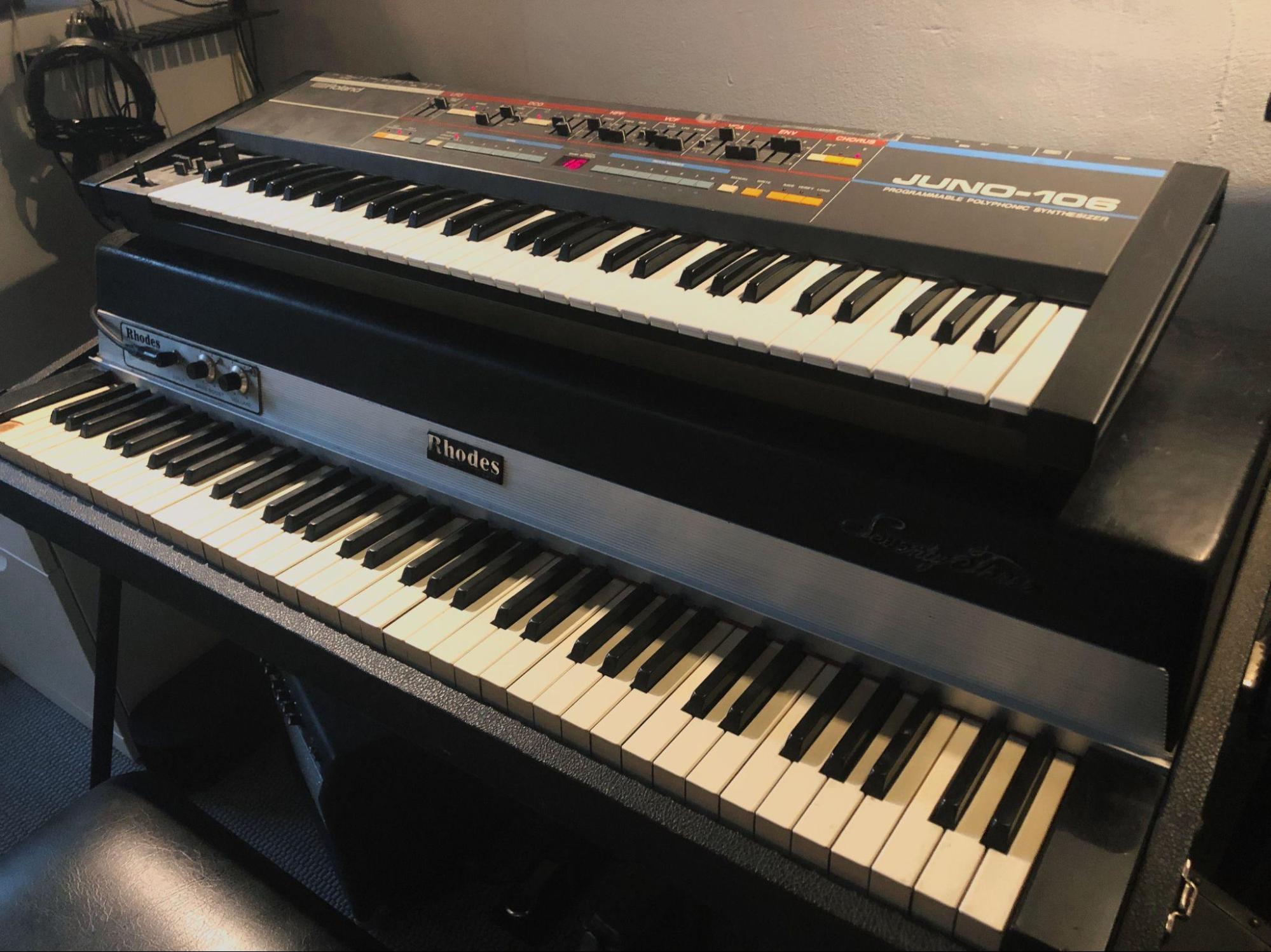
2. Do you have an ‘almost’ perfect bit of kit? What would you change?
Maybe my Juno 106. Great for bass, synth stabs, arps, pads.

3. What setup do you bring on holiday or tour or commute etc.?
Macbook Pro, 2 Samsung T2 SD’s (1 with samples and libraries. 1 with projects), Beyer Dynamics DT headphones, iRig midi keyboard with sustain.
A laptop. Ableton / Cubase. Headphones. Soft synths – Omnisphere, Zebra, Diva. NI Kontakt and some libraries.
If you’re into strings – Some of the Spitfire Audio sample libraries are pretty good. Small midi-keyboard (with sustain). And oh, just a quick tip about that…
If you play piano sounds on a small crappy non-weighted midi-keyboard, remember to use the velocity midi effect (in Ableton) on the track for playing with smoother velocities. Without it, it maxes out the vel. CCs real quick. Or a least that’s what it sounds like to me.
4. What software do you wish was hardware and vice versa?
Actually none I think. Every piece of hard- or software I have, is in the studio for a reason. After working almost exclusively in the box with soft synths and samples and FX in Ableton and Logic, for almost 15 years, I began to buy more physical gear. Mostly synths with analog circuits and my Space Echo RE-201. But with every piece of gear (hardware or software) in mind to cover different requirements.
Not because of better sound quality, since a lot of the “soft stuff” sounds amazing. But because of the tactile and more experimental experience of turning knobs and pushing faders.
I fucking love to put on the lab coat and just dive in and forget everything around me and just see where it takes me. If I pull up a soft synth, I get often inspired to make something, but I almost never get surprised. If I work on my Arp Odyssey, Lyra-8 or run stuff through my Clouds from Mutable Instruments, I get stuff I would never have dreamed of. It’s all the dirt, irregularities and happy accidents that I find interesting. It’s kind of more relatable on a both a mental and physical level. Specially as colours opposite to the more “clean” and “regular” stuff.
5. Is there anything you regret selling… or regret buying?
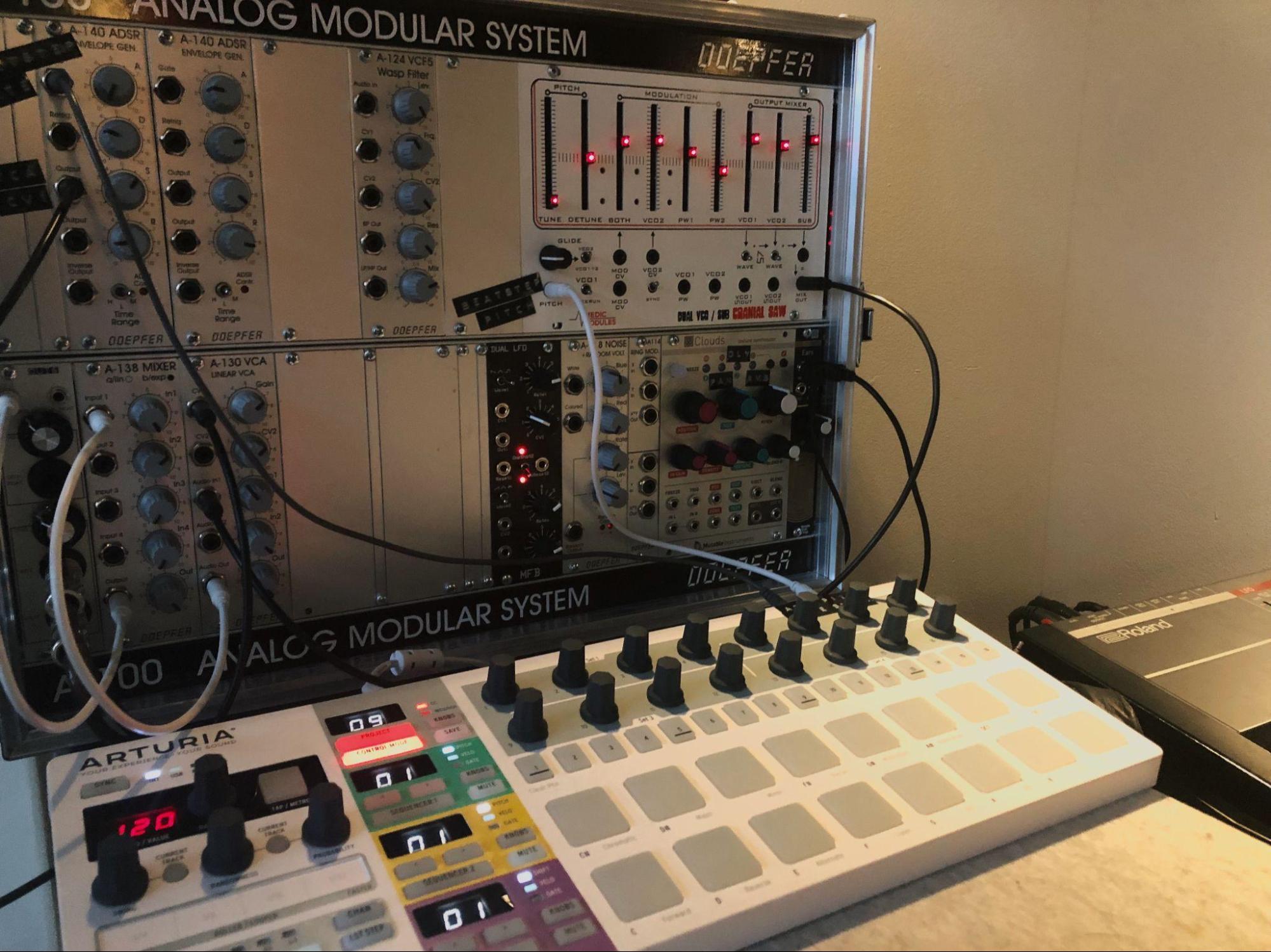

Can’t really justify how much I spend on my eurorack setup. It just doesn’t get used enough. Same goes for my Moog Sub37.
Sometimes I cheat and use a plug-in… Sorry.

But every time I do use it, specially for more distinct bass, its amazing with the live recorded filter modulation. Then the sound comes alive.
6. What gear has inspired you to produce the most music?’
On the “soft” side – Omnisphere, some Kontakt synths, Spitfire string libraries. Hardware – My Juno 106, the Arp Odyssey.
7. If you had to start over, what would you get first?
A wealthy girlfriend, cause this GAS is a sure way to be broke forever 🙂
8. What’s the most annoying piece of gear you have, that you just can’t live without?
My brain
Other than that… Can’t really think of one.
9. Most surprising tip or trick or technique that you’ve discovered about a bit of kit?
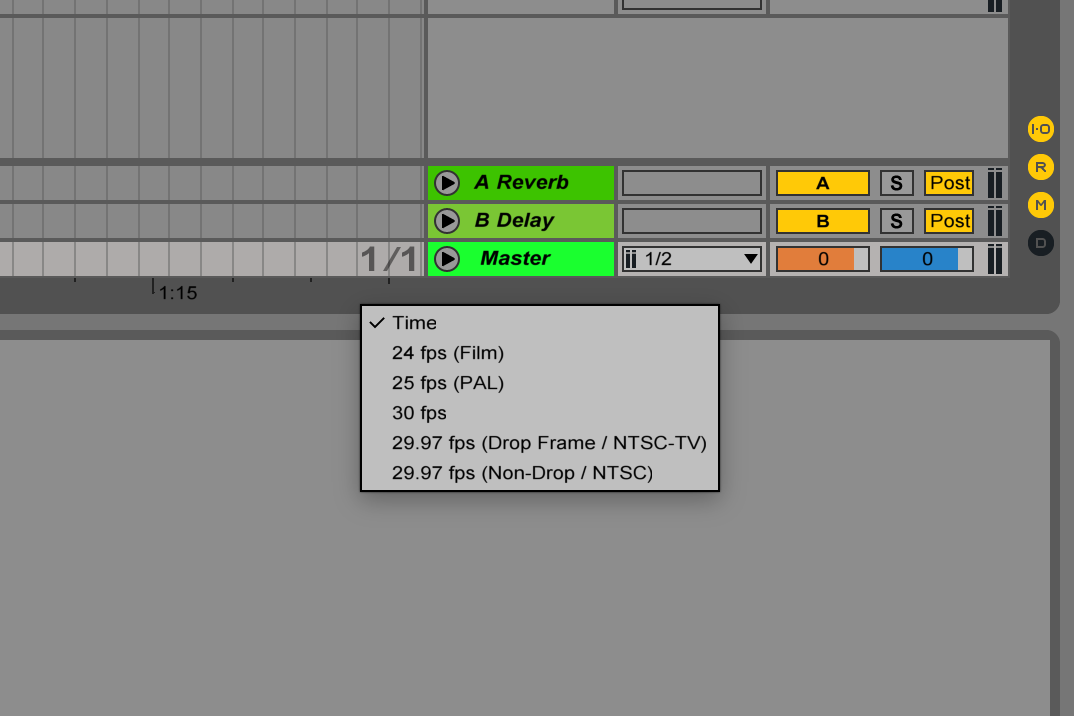
For those of you working to picture in Ableton. It’s actually possible to change the framerate. So the film and project are in sync.
Did my first feature film without knowing this and it fucked up the sync. After several YouTube deep dives, several years later (and after switching to Logic) I found a way.
Crtl and (left mouse click) in the timeline with min/ sec. = Choose framerate
Artist or Band name?
Martin Pedersen
Genre?
Electronic or hybrid film music – Meaning a blend of electronic and acoustic instruments, and organic elements.
Selfie?

Where are you from?
Copenhagen. But grew up in the south of Zealand. Moved back just before attending the Rhythmic Conservatory in CPH.
How did you get into music?
My parents doesn’t play music, but the radio was always on. I started playing saxophone at the age of 12 after watching a badass norwegian jazz quartet by chance on tv in my room.
Started making electronic music at 14 – SONY Acid Music Studio was the bomb back in the 90s. For me at least.
What still drives you to make music?
If I focus on my work in film. What drives me is, I just love storytelling SO much. Co-storytelling as a composer or just watching a film or a good show. Or just listening to a piece of music that can be a story on it’s own. It’s all about the emotional responds. To be totally immersed, letting everything else fade away around you. It all inspires my creative work and drives me to be a better storyteller. Film music or, the score, is a vital part of most film. I love amplifying the spirit of the film and storytelling with my music.
Music can reveal a films inner life in a way that can’t be fully articulated in any other way. It can have a telling effect on how the characters in the story come across – on how we perceive what they are feeling or thinking. The more engaging the drama – The truer the story becomes. Ok… I totally stole those lines from somebody. Can’t remember who… But I agree.
How do you most often start a new track?
Maybe a cool place to start is – How and when in the production phase I start composing the music for a new film or show.
Because it also relates to how I start a new track – Or “cue” – as it’s called in film.
When – It always starts with initial talks with the director. What is the heart of the story.
Are there musical references to draw from or is that up to me. And how do I translate that into what the DNA of the music will be. The earliest in the productions phase was composing after reading the script.
Working on the score for the first season of the tv-show “HOOLIGAN” I worked from the script and from dailies (unedited footage shot that day). That gives me an idea of the mood and tempo in the scene. How the camera is worked, the lighting and how the actors express themselves and interact with eachother.
Working on the score for the feature film “What Will People Say” I started working from scenes and a fully edited, but not picture locked film (Not locked meaning – most of the scenes are pretty much lined up, but not cut to the final length or order.)
How – I typically start with talks with the director about the story and the initial overall vibe.
Maybe also guided by musical references / tracks / cues. Parts of my score for the feature film “What We Become” was initially used as temp music in “What Will People Say”, before I was contacted to do the score. Temp (temporary) music is what the editor / director uses under scenes to “colour” the scene and drive it along. Temp can also help the composer to make a cue for a specific scene, that have a similar mood / function. Some composers love it. Others fucking hate it. I really don’t mind it. The hardest for me has been composing a new cue, from my own cues from other films used as temp. Making the cue kind of like it, but still sounding original for that specific project.
Hands on – I work in template in Logic. With everything set up with instrument groups, subgroups and fx groups.
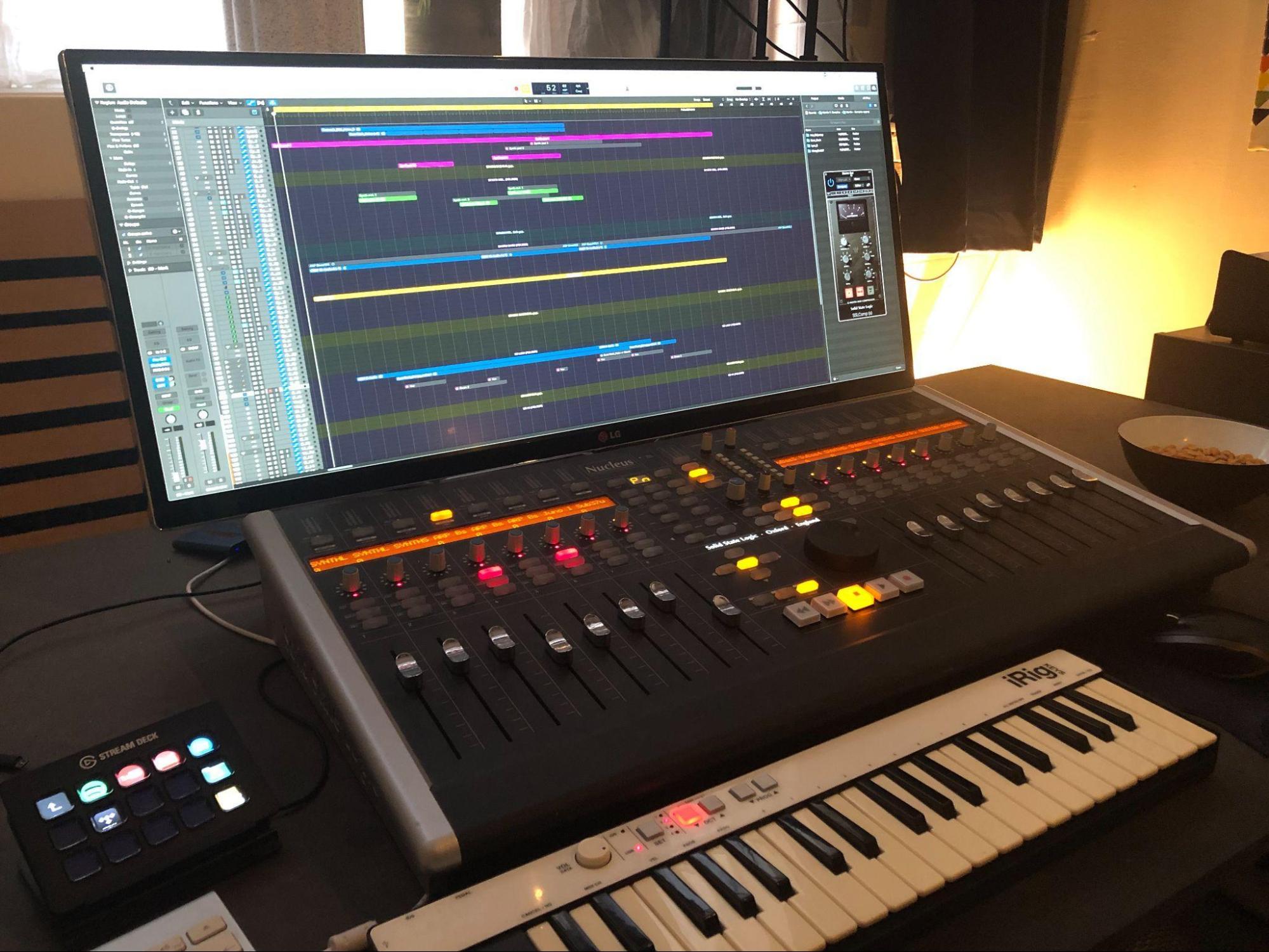

If it’s the first piece of music made for the film or show, I almost always open Logic. Look at the blank template. And go “Oh fuck, how do I do this? Maybe I should just find a job cutting grass or something more tangible. Normally that goes away quite fast.
I like to think about instrumentation and make sound palettes used in the specific project, before a single note is “written”.
During the process of working on the score, instruments and elements get cut out or added, defined by what the cues is made for if an instrument just doesn’t fit the overall vibe.
I do write themes. Sometimes from the beginning of the project. Just on a piano.
But often I’ll start with giving characters or elements in the film, specific individual soundpalettes. Or maybe a single instrument per character as a point of departure.
On a lot of scenes with underscoring, I start with a pad, evolving atmosphere or bass sound. “droney stuff” used as a bed for others elements.
Sometimes you need tempo driven elements to start it off. Arps or percussive elements. Sometimes a theme. I can start out with a massive sound in one scene. An almost do nothing in another. It’s all up to what serves the storytelling. And the film overall.
So the answer is… It depends. But I usually start every new track / cue with two questions – “What purpose does the music have in this scene? What is the feeling of the music in this scene?” And musically go from there.
I’m pretty heavy on the synth and electronic side. I use Omnisphere, Arturia Analog Lab and NI Kontakt libraries a lot.
So often I’ll set up interesting sounds within that. Some sounds from libraries. Other sounds are based on samples I’ve found, put into Omnisphere’s sampler and processed in different ways..
If a cue calls for something weirder like pitch-modulating or microtonal stuff, I usually start with using my analog synth’s – The Arp Odyssey or Lyra-8. If a scene calls for a more melancholic mood, I love using my Juno 106, for softer pads with a bit of modulating drift.
Fun fact – I often get inspired by working together with the sound designer on a film. Maybe they use some auditive elements – buzzing light fixtures or aircon sounds I dig. I then use that sound or something like it processed, as musical elements. When I did the score for the feature film “What We Become”, Peter Albrechtsen – the sound designer on the film, inspired me a lot.
I incorporated some of his sounds used as musical components. It glues the music and sound design well together.
I especially dig the primary sound in the musical palette of the SWAT team. That sound was initially made out of a metal chair being dragged over a concrete floor in an very large room. So sometimes my cues starts with a “real” sound that’s been processed.
How do you know when a track is finished?
When nothing weird sticks out, the scene moves along and you are engaged all the way. On a more overall view. A film is never finished. It premieres. Meaning you have until your deadline… Then it’s finished no matter what.
Show us your current studio
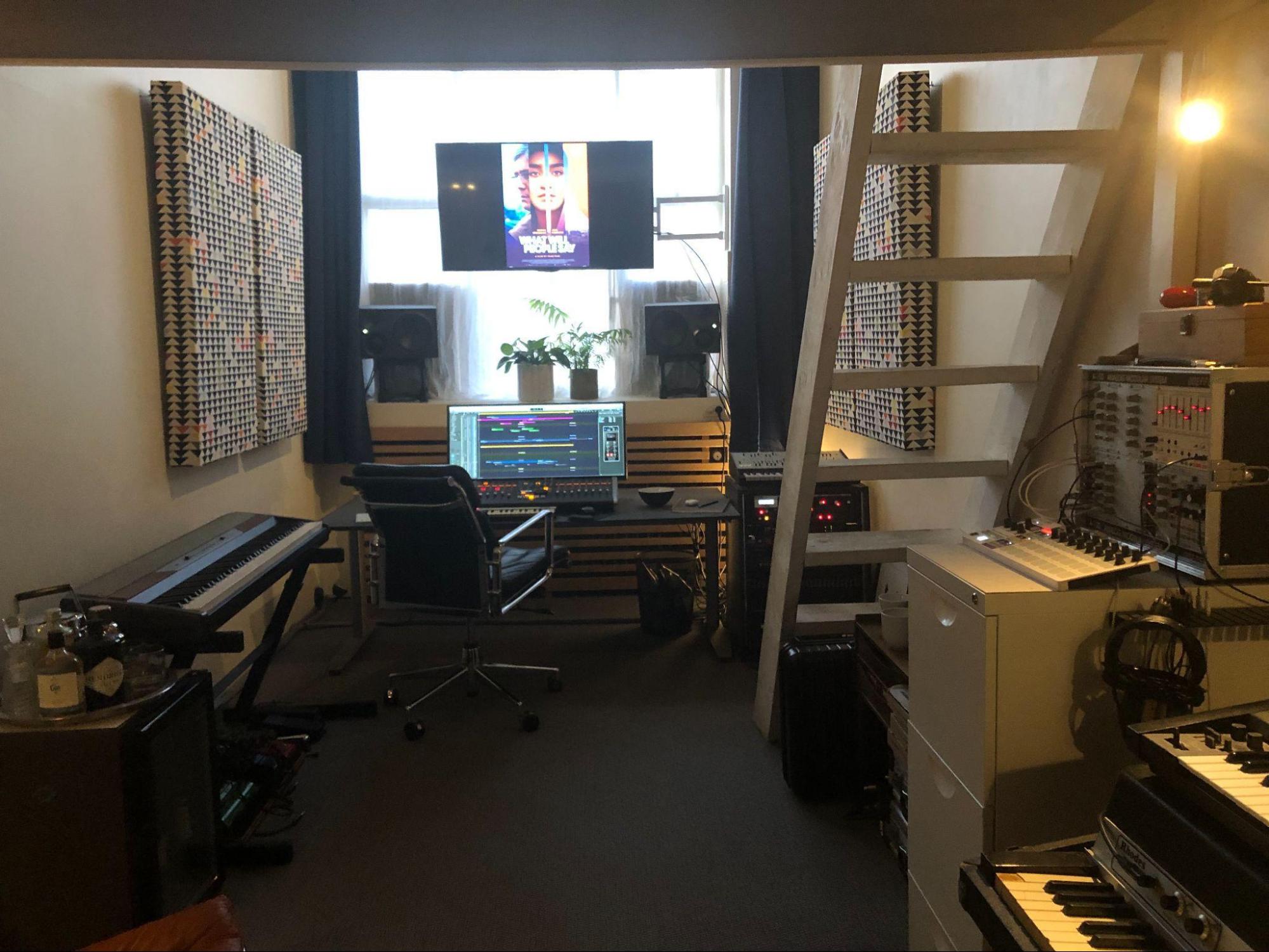
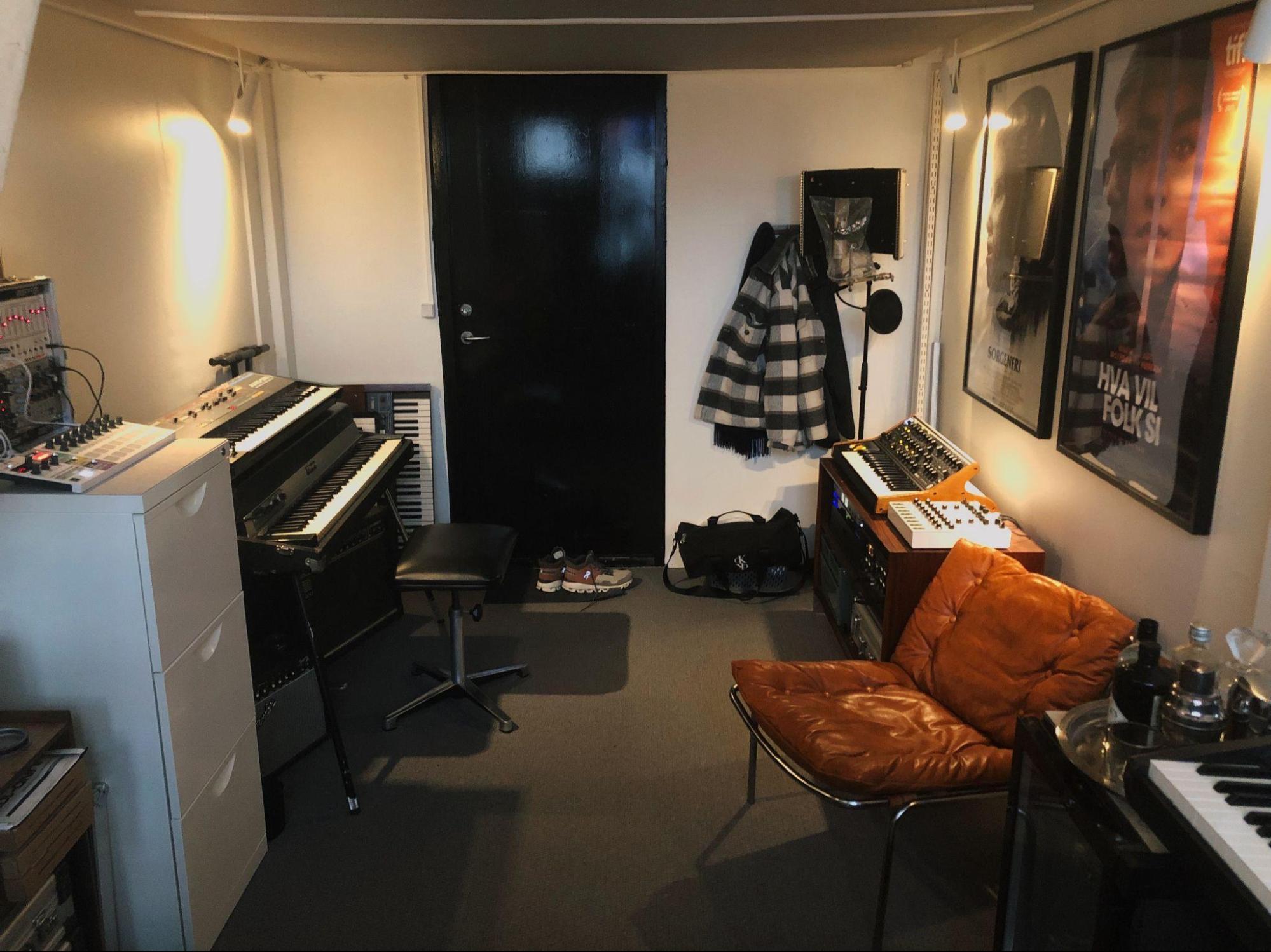
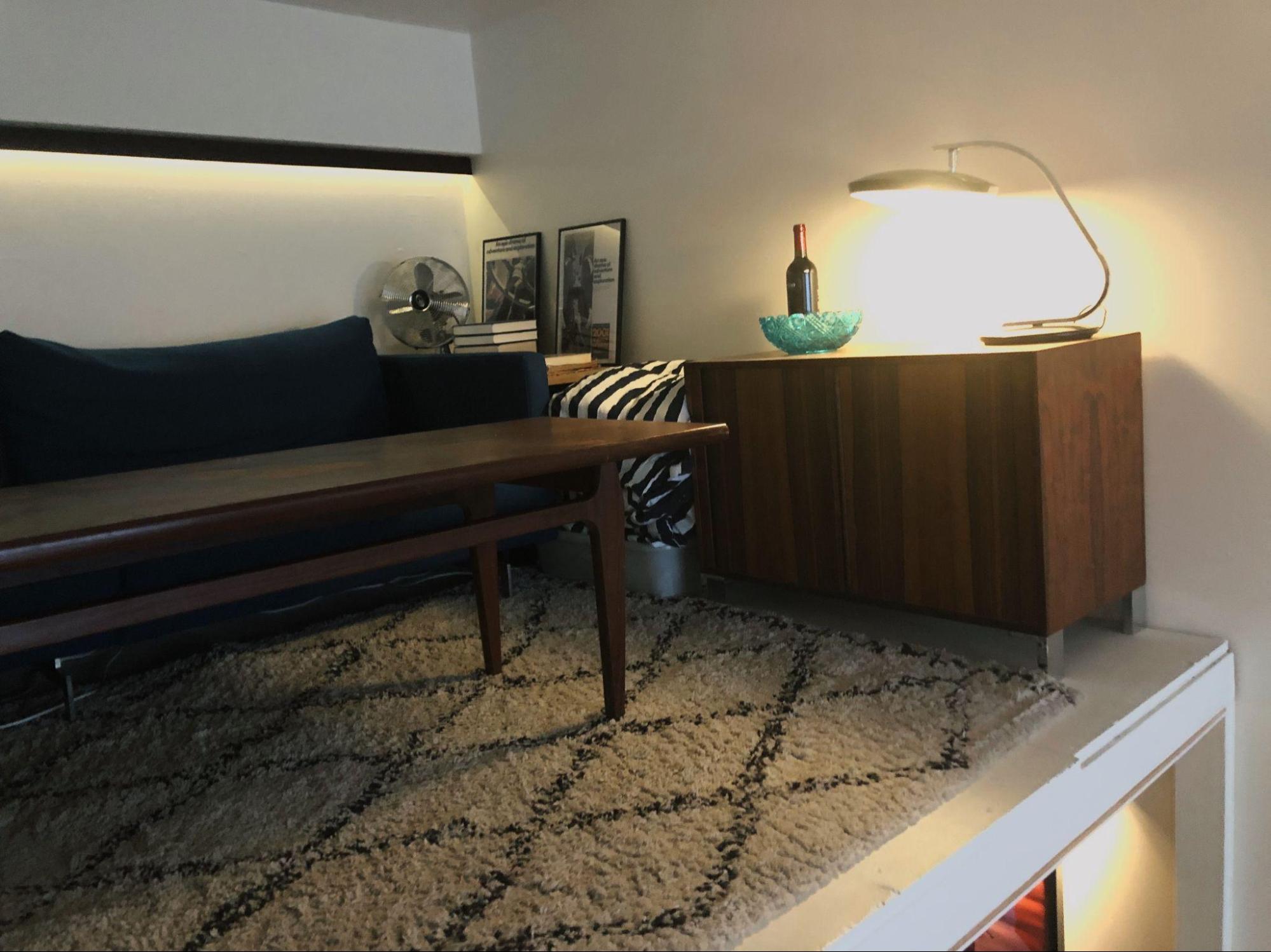



Best creative advice that you’ve ever heard?
Love what you do. And try out new stuff.
A new approach to the material – Like working with certain dogmas, new gear, a new instrument. Listen to genres you normally don’t do. Things that pushes you out of your typical musical comfort zone. The more I learn, the more I keep re-falling in love with music.
Promote your latest thing… Go ahead, throw us a link.
One of the bigger recent things I’ve done is the tv-show “HOOLIGAN” season 1.
These days I’m working on my second album titled “COCOON”. Release later this year. Spotify
[Editor: You can find more about Martin at his site www.composermartinpedersen.com]
[Editor: There are affiliate links to the relevant gear throughout the articles. It helps to support this blog. In fact, should you be needing some patch cables or guitar strings. Then clicking on one of the above links and buying any product that you prefer, will help the blog… doesn’t even have to be the ones in the link. Thx]







